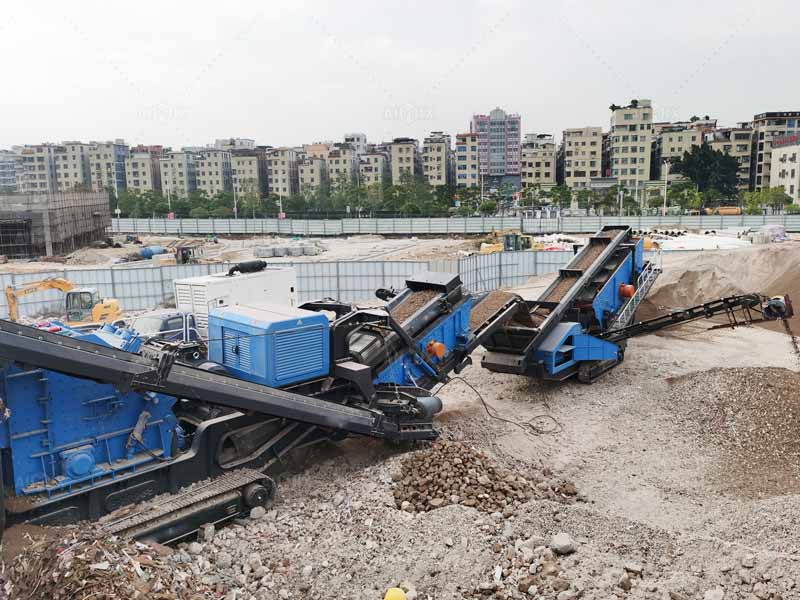
To know how to crush rocks, we first understand why we need to crush rocks, only fully understand the importance and role of crushing rocks for various fields, in order to choose the most suitable crushing method for your project according to these.
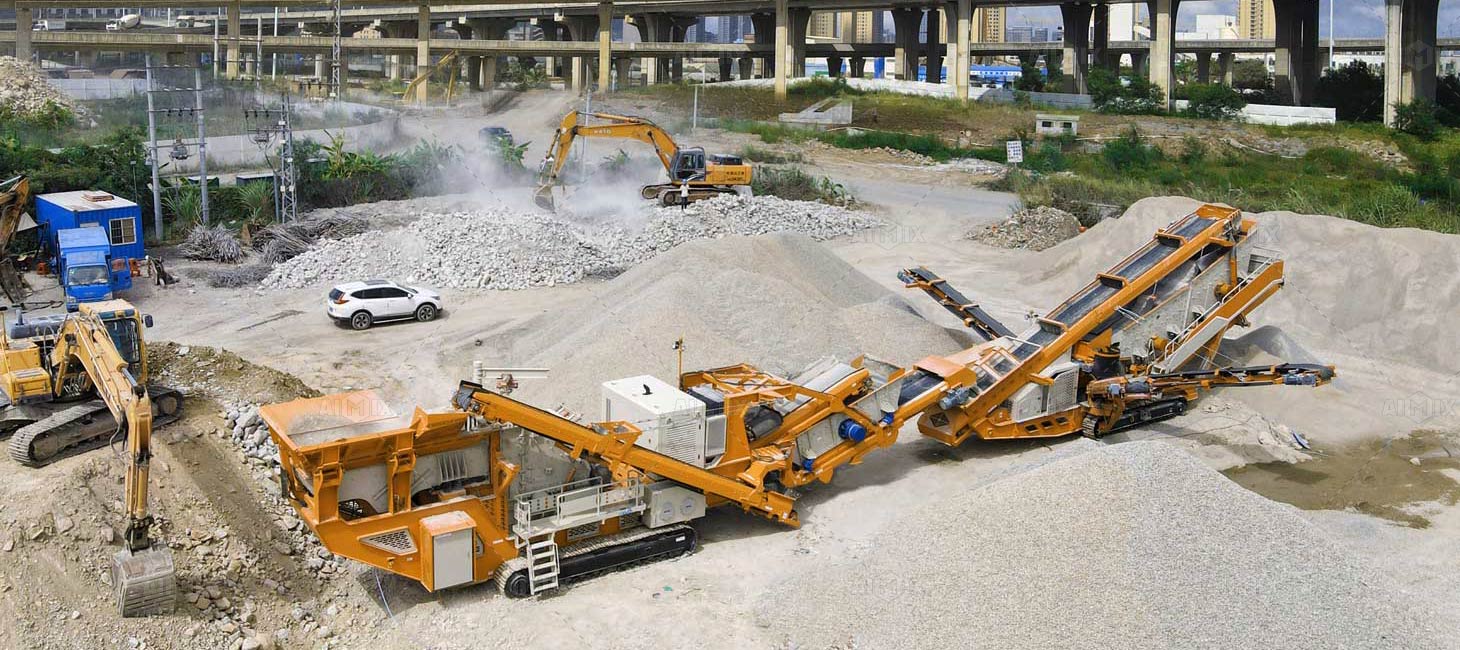





Crushing rock for the promotion of economic development, resource utilization, environmental protection and scientific research are of great significance, mainly from 7 aspects to take you to understand the wonders.
7 Dimensions Take You To Appreciate The Value Of Rock Crushing!
Construction and infrastructure development
Crushed rock is used to manufacture construction materials such as concrete, bricks, stones, etc., which are used to build various infrastructures such as houses, bridges, roads, tunnels and so on.
Material Processing
In the construction, manufacturing and processing industries, rocks need to be processed into materials of different shapes and sizes, such as gravel, sandstone, limestone, etc., to meet specific engineering needs.
Mining and Resource Extraction
In the mining industry, crushing rock is a key step in the extraction of ores. By crushing rocks, various mineral resources such as metal ores, coal, oil and gas can be obtained.
Civil engineering and building construction
Crushed rock is used in various stages of civil engineering projects such as foundation treatment, retaining wall construction, road paving, subway tunnel excavation and so on.
Resource Recycling
Discarded rocks or construction waste can be converted into reusable resources through crushing and reprocessing, promoting resource recycling and sustainable environmental development.
Environmental engineering
In the field of civil engineering and environmental protection, rock crushing and processing are required for land remediation, environmental management and infrastructure construction, such as the construction of retaining walls and river training.
Geological research
Rock crushing and analysis can help geologists understand the geological structure, stratigraphic features and the process of earth evolution, thus promoting the research and understanding of earth science.
6 Ways To Crush Rocks
Is it possible to crush a rock? Sure, there are six ways to crush rocks, here I will share with you.
Mechanical crushing
Mechanical equipment is used to break rock by applying pressure or impact to the rock. This includes:
- Jaw crusher: utilizes two symmetrical jaws to squeeze and crush the rock.
- Cone Crusher: squeezes and crushes rock by means of a conical crushing head and wall.
- Impact Crusher: utilizes a high-speed rotor to apply impact force to the rock to break it into smaller particles.
Blasting
The use of explosives or blasting agents to create an explosion within the rock, causing it to break and shatter. Blasting is typically used in large-scale mining or civil engineering projects.
Chemical fragmentation
The use of chemical solvents or acids to dissolve the structure of the rock, causing it to break up or become easier to handle. This method is usually used for specific types of rock, such as limestone.
Thermal Breaking
Treating rock at high temperatures to cause it to swell, crack or become easier to break. Thermal crushing can be achieved by heating or cooling.
Vibratory crushing
Vibratory equipment is used to apply vibratory forces to rock to break it into smaller particles. This method is typically used for fine crushing of rock, such as for the production of sand and gravel.
Hydrocrushing
The use of hydraulic pressure to break rock into smaller particles. Hydrocrushing is usually used in excavation work and tunnel construction.
The most common method of rock crushing is by mechanical means, using equipment such as crushers, jaw crushers, impact crushers or cone crushers. These machines apply force to the rock by compression, impact or shear to break it into smaller pieces. Crushers come in a variety of sizes and configurations to suit different types of rock and production requirements. You can learn more about selection guide from this page: How To Choose a Rock Crusher.
Specifications
| Model | APY2-57J | APY2-69J | APY2-750J | APY2-110J |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feeder model | APG-3090W | APG-3896W | APG-4211W | APG-4211W |
| Crusher model | APJ-5075E | APJ-6090E | APJ-7510E | APJ-110V |
| Maximum feed size (mm) | 425 | 500 | 630 | 650 |
| Silo volume (m3) | 4 | 5.3 | 7 | 7 |
| Iron separator model (optional) | RCYD(C)-6.5 | RCYD(C)-6.5 | RCYD(C)-8 | RCYD(C)-12 |
| Tire configuration | Parallel double shaft | Parallel double shaft | Parallel three shafts | Parallel three shafts |
| Main belt conveyor model | B650×8.5m | B800×8.5m | B1000×10m | B1000×10m |
| Side out belt conveyor model (optional) | B500×4m | B500×4m | B650×5m | B650×5m |
| Generator power (kW) (optional) | 120 | 160 | 200 | 250 |
| Production capacity (t/h) | 45-100 | 60-160 | 110-320 | 250-400 |
| Transport Length (mm) | 12500 | 12750 | 13270 | 13200 |
| Transport width (mm) | 2600 | 2600 | 2850 | 3000 |
| Transport height (mm) | 3950 | 3950 | 4200 | 4400 |
| Weight (t) | 28 | 39 | 57 | 65 |
| Model | APY2-110C | APY2-160C | APY2-200C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Crusher model | APC-110C | APC-160C | APC-200C |
| Vibrating screen model | APS-1848Y | APS-1860Y | APS-2160Y |
| Maximum feed size (mm) | 160 | 200 | 215 |
| Tire configuration | Parallel double shaft | Parallel double shaft | Parallel double shaft |
| Feeding belt conveyor model (optional) | B650 | B800 | B1000 |
| Output belt conveyor model (optional) | B500 | B650 | B650 |
| Under-sieve belt conveyor model | B650 | B800 | B1000 |
| Generator power (kW) (optional) | 240 | 280 | 320 |
| Production capacity (t/h) | 50-230 | 80-390 | 120-420 |
| Transport Length (mm) | 13800 | 13800 | 14500 |
| Transport width (mm) | 3000 | 3000 | 3000 |
| Transport height (mm) | 4400 | 4400 | 4500 |
| Weight (t) | 32 | 37 | 42 |
| Model | APY3-1010F | APY3-1210F | APY3-1214F | APY3-1315F |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feeder model | APG-3090W | APG-3896W | APG-3896W | APG-4211W |
| Crusher model | APF-1010H | APF-1210H | APF-1214H | APF-1315H |
| Vibrating screen model | APS-1548Y | APS-1848Y | APS-1860Y | APS-2160Y |
| Tire configuration | Parallel three shafts | Parallel three shafts | Parallel three shafts | Parallel three shafts |
| Return belt conveyor model | B650 | B650 | B800 | B1000 |
| Feeder belt conveyor model | B650 | B800 | B800 | B1000 |
| Under-sieve belt conveyor model | B800 | B800 | B1000 | B1000 |
| Production capacity (t/h) | 70-150 | 100-285 | 150-350 | 180-500 |
| Transport length (mm) | 13000 | 15800 | 15800 | 16500 |
| Transport width (mm) | 2500 | 2550 | 2550 | 3000 |
| Transport height (mm) | 4200 | 4500 | 4500 | 4500 |
| Weight (t) | 41 | 45 | 53 | 60 |
The Best Way to Crush Rock
Determining which rock crushing method is best depends on the specific situation and needs. There is no one method that is suitable for all situations, but rather the evaluation and selection is based on several factors:
-
Nature of the rock
Different types of rock have different hardnesses, strengths and structures. Certain rocks may be more suitable for mechanical crushing while others may be more suitable for blasting or chemical crushing. Therefore, the nature of the rock needs to be understood first to determine the most suitable crushing method.
-
Required particle size and throughput
Depending on the required end product size and throughput, the appropriate crushing method is selected. Some methods make it easier to control size and throughput, while others are more suitable for large-scale, high-throughput crushing operations.
-
Cost and efficiency
Consider the cost and efficiency of various crushing methods. This includes equipment costs, energy consumption, labor costs, and maintenance and operating costs. Choosing the most cost-effective method can reduce production costs and increase profits.
-
Environmental impact
Evaluate the environmental impact of various crushing methods, including noise, vibration, dust and waste generation. Choosing the method with less environmental impact can reduce environmental pollution and meet the requirements of sustainable development.
-
Safety
Consider the safety of various crushing methods for personnel and equipment. Some methods may carry high safety risks, such as blasting, and therefore require strict safety measures to protect staff.
In practice, a combination or adjustment of multiple crushing methods may be required to achieve the best crushing effect. Today we take mechanical crushing as an example and look at the uses for which it is suitable.
Pros and Cons of Mechanical Crushing
Mechanical crushing, a common method of rock treatment, has a range of pros and cons. Below are the main pros and cons of mechanical crushing:
- Efficient production: mechanical crushing equipment can efficiently process large quantities of rock, increasing productivity and output.
- Controllable particle size: by adjusting the parameters of mechanical equipment, the size of the rock particles obtained can be controlled to meet the needs of different applications.
- Widely applicable: mechanical crushing is applicable to various types and hardness of rocks, and can be flexibly applied to different rock processing needs.
- Lower cost: Compared with some other crushing methods, mechanical crushing usually has lower cost, especially in small and medium-sized crushing tasks.
- Reliable and stable: mechanical crushing equipment is usually simple in structure, stable in operation, not easily affected by external factors, and has high reliability.
- Higher energy consumption: mechanical crushing requires a lot of energy consumption, especially in large-scale production tasks, which may lead to higher energy costs.
- Noise and vibration: mechanical crushing equipment generates noise and vibration during operation, which may cause disturbance to the surrounding environment and staff.
- Dust pollution: Dust generated during the mechanical crushing process may have an impact on air quality, as well as on the working environment and staff health.
- Equipment Maintenance: Mechanical crushing equipment requires regular maintenance and upkeep to ensure its normal operation and prolong its service life, which will increase operating costs and management difficulties.
How To Deal With The Negative Impact Of Crushing Rock
Dealing with the negative impact of crushing rock involves implementing various strategies to mitigate its adverse effects on the environment, communities, and public health. Here are some measures that can be taken to address these impacts:
Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA):
Conducting a comprehensive environmental impact assessment before starting rock crushing operations can help identify potential environmental risks and develop appropriate mitigation measures. This assessment should evaluate factors such as air quality, noise pollution, water pollution, habitat disruption, and soil erosion.
Site Selection and Planning:
Choose rock crushing sites away from sensitive ecosystems, residential areas, and protected areas whenever possible. Proper site planning and layout design can help minimize environmental impacts and reduce potential conflicts with surrounding communities.
Dust Suppression:
Implement effective dust suppression measures to minimize the release of dust particles into the air during crushing operations. This can include using water sprays, dust suppression systems, or enclosing the crushing area with barriers to contain dust.
Noise Control:
Employ noise control measures such as noise barriers, mufflers, or sound-absorbing materials to reduce noise levels generated by rock crushing activities. Additionally, scheduling crushing operations during off-peak hours and using quieter equipment can help minimize noise disturbances to nearby communities.
Water Management:
Manage water usage responsibly to prevent excessive water consumption and minimize the risk of water pollution. Implement water recycling systems, use environmentally friendly water treatment methods, and prevent runoff of contaminated water into nearby water bodies.
Waste Management:
Properly manage waste materials generated during rock crushing, including segregating and disposing of waste materials such as concrete, asphalt, and other construction debris in accordance with regulations. Recycling and reusing these materials whenever possible can help reduce waste generation and minimize environmental impact.
Erosion and Sediment Control:
Implement erosion and sediment control measures to prevent soil erosion and sediment runoff from the crushing site. This can include revegetation, erosion control blankets, silt fences, and other erosion control practices to stabilize soil and prevent sediment pollution of nearby water bodies.
Community Engagement and Communication:
Engage with local communities, stakeholders, and regulatory agencies to address concerns, gather feedback, and foster transparency and trust. Communication and collaboration with stakeholders can help identify potential issues early and develop mutually acceptable solutions.
Compliance with Regulations:
Ensure compliance with environmental regulations, permits, and standards applicable to rock crushing operations. This may involve obtaining necessary permits for air and water emissions, complying with noise regulations, and conducting regular monitoring to assess compliance with environmental requirements.
Continuous Monitoring and Improvement:
Regularly monitor environmental performance, assess the effectiveness of mitigation measures, and make necessary adjustments to minimize environmental impacts. Continuous improvement and adaptive management are essential to mitigate the adverse effects of rock crushing activities over time.
The Cost Of Rock Crushing
Equipment cost
The equipment needed for rock crushing includes crusher, vibrating screen, conveying equipment and so on. The acquisition cost of equipment depends on factors such as equipment type, size, brand and technical level.
Energy consumption
The process of rock crushing needs to consume a lot of energy, mainly including electricity and fuel. Energy cost is affected by energy price, equipment efficiency and production process.
Labor cost
The process of rock crushing requires manpower to operate and manage the equipment, labor costs include wages, training and management costs.
Raw material costs
The rock crushing process may require the use of some raw materials and chemicals, such as lubricants, lubricants, etc., and these raw material costs need to be included in the total cost.
Maintenance and Repair Costs
Regular maintenance and repair of the equipment to ensure its normal operation is essential, maintenance and repair costs, including parts replacement, maintenance personnel wages and other costs.
Transportation cost
After crushing the rock, it needs to be transported to the destination, and the transportation cost depends on the transportation distance, transportation mode and transportation market price and other factors.
Environmental protection costs
In order to comply with environmental regulations and standards, it may be necessary to invest in the purchase of environmental protection equipment or the implementation of environmental protection measures, these costs also need to be included in the total cost.
Management and administration costs
Management and administration costs include the costs of equipment management, personnel management, financial management, etc., which are not to be ignored in the total cost.
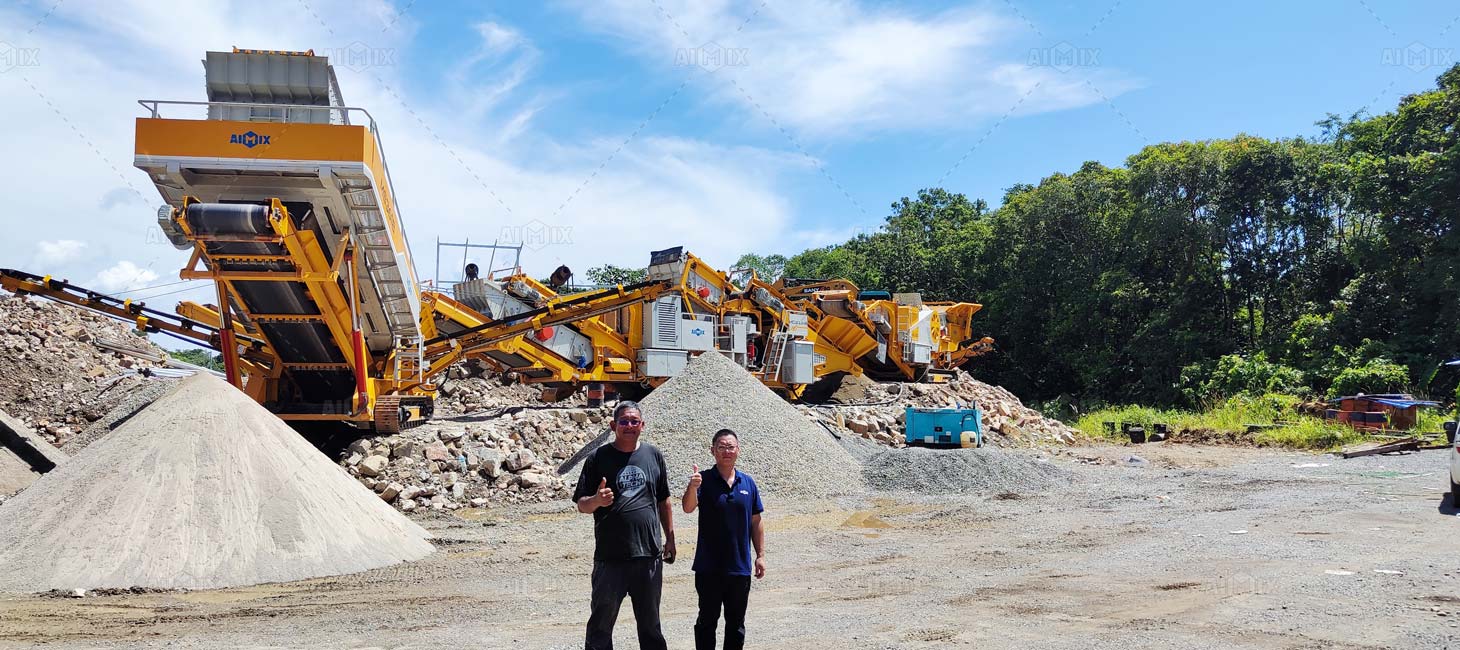

FAQs About Crushing Rocks
Q: Which crusher is suitable for your hard rock
A: The choice of hard rock crusher depends on factors such as rock hardness, required output and desired product size. Common choices include jaw crushers for primary crushing, cone crushers for secondary or tertiary crushing, and impact crushers for shaping aggregates. Gyratory crushers are suitable for large-scale mining operations. Consulting with an expert can help determine the best crusher for your specific needs.
Q: How to crush rocks into gravel
A: To crush rocks into gravel, you typically use a crushing machine such as a jaw crusher, impact crusher, or cone crusher machine. These machines break down large rocks into smaller pieces, which are then sorted and screened to create gravel of various sizes.
Q: How do you crush rock manually
A: Manually crushing rock typically involves using a hammer or a sledgehammer to break the rock into smaller pieces. This method requires physical strength and can be time-consuming.
Q: What can i use to crush rocks or granite
A: For crushing rocks or granite, you can use equipment such as jaw crushers, cone crushers, or impact crusher plant. These machines are commonly used in various applications to break down hard rock into smaller pieces.
Q: How to crush rocks into powder
A: To crush rocks into powder, you can use a crusher or mortar and pestle. A crusher will mechanically break down the rocks into smaller pieces, while a mortar and pestle provide a manual method for grinding rocks into powder. Both methods can be effective depending on the type of rock and the desired fineness of the powder.
Q: How to crush rocks into gravel at home
A: To crush rocks into gravel at home, you can use a variety of methods: manual crushing, DIY rock crusher, rock tumbler, mortar and pestle, and mechanical crusher.
In conclusion, whichever method is used, safety must come first when crushing rock, with due consideration of factors such as environmental impact and cost-effectiveness. The most important thing is to find a professional manufacturer should evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the chosen method to ensure the best utilization of resources and the overall efficiency of the rock crushing operation. AIMIX will be waiting for you!